Even though people learn the English language since their childhood, they are hardly aware of its origin of it. As we all know English is the lingua franca, the language which is used commonly all over the world. English takes its place as one of the world’s predominant forms of communication with its influences extending over as many as two billion people globally.
The English language itself really took off with the invasion of Britain during the 5th century. Three Germanic tribes, the Jutes, Saxons, and Angles were seeking new lands to conquer and crossed over from the North Sea. During the invasion, the native Britons were driven north and west into lands that are referred to as Scotland, Ireland, and Wales. The word England and English originated from the Old English word Engla- land, literally meaning “the land of the Angles” where they spoke Englisċ (Old English).
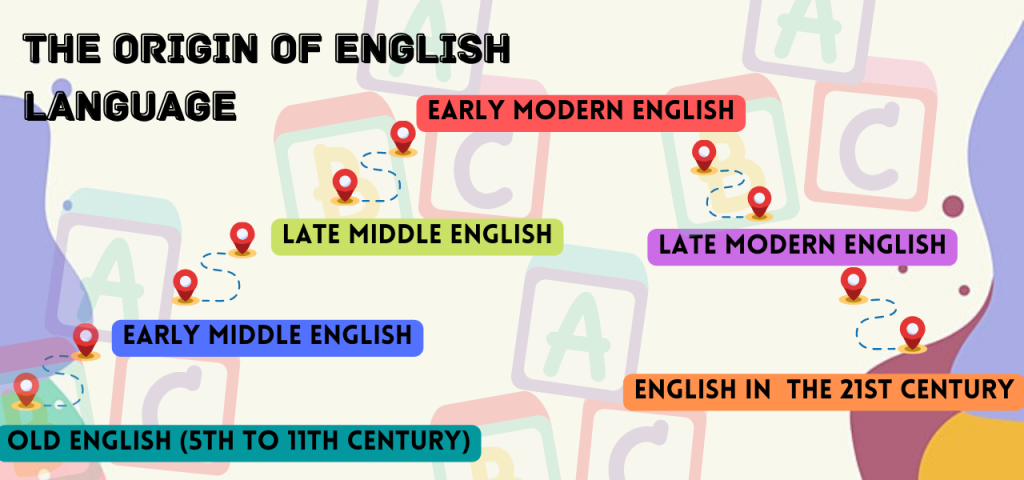
The origin of the English language can be divided as below:
- Old English (5th to 11th century)
- Prehistoric or Primitive (5th to 7th century)
- Early Old English (7th to 10th century)
- Late Old English (10th to 11th century)
- Early Middle English (1100-1250)
- Late Middle English (1400-1500)
- Early Modern English (end of the fifteenth century)
- Late Modern English (1800 – present)
- English in the 21st century
It is significant to discuss on above eras in detail.
It is discussed that Old English is divided into three main parts. They are Prehistoric, Early Old English and Late Old English. There is no literature or documentation aside from referencing the Prehistoric period. One can find limited examples of Anglo-Saxon runes. The Early Old English period contains some of the earliest documented evidence of the English language, showcasing notable authors and poets like Cynewulf and Aldhelm who were leading figures in the world of Anglo-Saxon literature. Late Old English can be considered as the final phase of the Old English language which was brought about by the Norman invasion of England. This period ended with the consequential evolution of the English language towards Early Middle English.
English language and grammar started evolving with particular attention to syntax in the Early Middle English period. It can be found that while the British government and its wealthy citizens Anglicised the language, Norman and French influences remained the dominant language until the 14th century. Moreover, this period has been attributed with the loss of case endings that ultimately resulted in inflection markers being replaced by more complex features of the language.
It was during the mid-1400s that the Chancery English standard was brought about. The clerks working for the Chancery in London were fluent in both French and Latin. It was their job to prepare official court documents and prior to the 1430s both the aforementioned languages were mainly used by royalty, the church, and wealthy Britons. After this date the clerks started using a dialect that sounded as follows;
- Gaf (gave) not yaf (Chaucer’s East Midland dialect)
- Such not swich
- They’re (their) not hir
As one can notice the above is starting to sound more like the present-day English language as we all know.
The changes in the Early Modern English period are pronunciation, vocabulary and grammar and also the start of the English Renaissance. The English Renaissance has much quieter foundations than its pan-European cousin, the Italian Renaissance and sprouted during the end of the 15th century. It was associated with the rebirth of societal and cultural movements. The first successful English colony was established in the 17th century and it was called The New World. Literary classics like those of John Milton’s Paradise Lost were published in this age.
When it comes to the Late Modern English period, the industrial revolution and the rise of the British Empire are the major incidents and people can note the expansion of the English Language. Due to the industrial revolution, human beings invented advanced technologies and different types of scientific productions. Because of this, people wanted new words and phrases and concepts to describe and store the theoretical analysis of the products. Therefore, scientists and scholars created words using Greek and Latin roots as bacteria, histology, nuclear, and biology. The English language has some borrowed words due to colonial Britain. Now, people use the modern English language and it can be found some discrepancies even in modern English.
The basic history and development of a language that literally spawned from the embers of wars fought between ferocious civilizations. So, any language has its own stages when developing. It is the same for the English language as any other language in the world.


